Problem-Solving: Fall-2025
W3D2 Practice : Due W3 D2
- Find Area/Volume from the Vector Differential
S0 5407S
Start with \(d\vec{r}\) in rectangular, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Use these expressions to write the scalar area elements \(dA\) (for different coordinate equals constant surfaces) and the volume element \(d\tau\). It might help you to think of the following surfaces: The various sides of a rectangular box, a finite cylinder with a top and a bottom, a half cylinder, and a hemisphere with both a curved and a flat side, and a cone.
- Rectangular: \begin{align} dA&=\\ d\tau&= \end{align}
- Cylindrical: \begin{align} dA&=\\ d\tau&= \end{align}
- Spherical: \begin{align} dA&=\\ d\tau&= \end{align}
- Flux through a Cylinder
S0 5407S
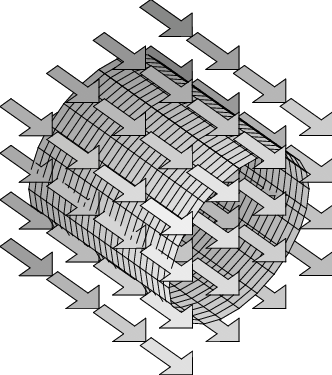
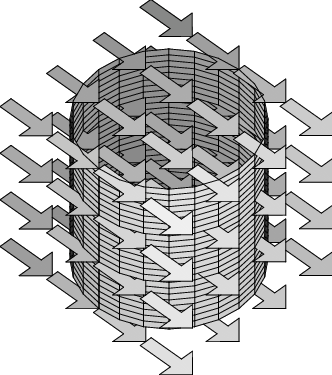
- What do you think will be the flux through the cylindrical surface that is placed as shown in the constant vector field in the first figure?
- What if the cylinder is placed upright, as shown in the second figure? Explain.